中国沙漠 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 262-274.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2025.00002
• • 上一篇
刘永杰1,2( ), 杜鹤强1(
), 杜鹤强1( ), 范亚伟1,2, 杨胜飞1,2
), 范亚伟1,2, 杨胜飞1,2
收稿日期:2024-11-18
修回日期:2025-01-01
出版日期:2025-03-20
发布日期:2025-03-26
通讯作者:
杜鹤强
作者简介:刘永杰(2001—),女,重庆人,硕士研究生,主要从事荒漠化遥感监测方面的研究。E-mail: 19122740412@163.com
基金资助:
Yongjie Liu1,2( ), Heqiang Du1(
), Heqiang Du1( ), Yawei Fan1,2, Shengfei Yang1,2
), Yawei Fan1,2, Shengfei Yang1,2
Received:2024-11-18
Revised:2025-01-01
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-03-26
Contact:
Heqiang Du
摘要:
荒漠化发展使毛乌素沙地生态环境面临严峻挑战。当前荒漠化监测存在目视解译主观性强、数据更新慢等问题。因此,亟待发展客观、快速的荒漠化定量监测手段。随着遥感云计算的出现与发展,Google Earth Engine (GEE)平台不仅提供多源遥感信息数据,还具备高效的计算性能,为荒漠化快速监测创造了条件。基于GEE平台和Landsat影像,构建毛乌素沙地2000—2022年Albedo-NDVI特征空间模型,并利用地理探测器模型定量分析影响其荒漠化演变的驱动力因素。结果表明:(1)2000—2022年,毛乌素沙地荒漠化趋势整体逆转,轻度荒漠化和非荒漠化面积逐年增加,且恢复区域面积大于退化区域。空间分布呈现明显的异质性,西北部荒漠化程度较重,东南部荒漠化程度较轻且逆转较快。(2)毛乌素沙地荒漠化演变是多种因素共同作用的结果,降水量和GDP因子解释力排名位居前列,q值平均值均较高于其他因子,分别为0.078和0.105,是影响毛乌素沙地荒漠化的主要驱动因子。
中图分类号:
刘永杰, 杜鹤强, 范亚伟, 杨胜飞. 基于Google Earth Engine(GEE)的毛乌素沙地风蚀荒漠化过程监测[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(2): 262-274.
Yongjie Liu, Heqiang Du, Yawei Fan, Shengfei Yang. Monitoring of wind erosion desertification process in the Mu Us Desert based on Google Earth Engine (GEE)[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(2): 262-274.
| 年份 | 荒漠化程度 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 极重度荒漠化 | 重度荒漠化 | 中度荒漠化 | 轻度荒漠化 | 非荒漠化 | |
| 2000 | ≤-0.38 | -0.38~0.36 | 0.36~0.62 | 0.62~0.95 | ≥0.95 |
| 2005 | ≤-0.29 | -0.29~0.75 | 0.75~1.30 | 1.30~2.13 | ≥2.13 |
| 2010 | ≤-0.05 | -0.05~1.30 | 1.30~2.07 | 2.07~3.15 | ≥3.15 |
| 2015 | ≤-0.40 | -0.40~0.19 | 0.19~0.41 | 0.41~0.73 | ≥0.73 |
| 2020 | ≤-0.27 | -0.27~0.51 | 0.51~0.90 | 0.90~1.42 | ≥1.42 |
| 2022 | ≤-0.33 | -0.33~0.72 | 0.72~1.22 | 1.22~1.84 | ≥1.84 |
表1 2000—2022年毛乌素沙地荒漠化差值指数( DDI )分级
Table 1 Desertification Difference Index ( DDI ) classification table of the Mu Us Desert from 2000 to 2022
| 年份 | 荒漠化程度 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 极重度荒漠化 | 重度荒漠化 | 中度荒漠化 | 轻度荒漠化 | 非荒漠化 | |
| 2000 | ≤-0.38 | -0.38~0.36 | 0.36~0.62 | 0.62~0.95 | ≥0.95 |
| 2005 | ≤-0.29 | -0.29~0.75 | 0.75~1.30 | 1.30~2.13 | ≥2.13 |
| 2010 | ≤-0.05 | -0.05~1.30 | 1.30~2.07 | 2.07~3.15 | ≥3.15 |
| 2015 | ≤-0.40 | -0.40~0.19 | 0.19~0.41 | 0.41~0.73 | ≥0.73 |
| 2020 | ≤-0.27 | -0.27~0.51 | 0.51~0.90 | 0.90~1.42 | ≥1.42 |
| 2022 | ≤-0.33 | -0.33~0.72 | 0.72~1.22 | 1.22~1.84 | ≥1.84 |
| 判断标准 | 交互作用类型 |
|---|---|
| q(X1∩X2)<Min(q(X1),q(X2)) | 非线性减弱 |
| Min(q(X1),q(X2))<q(X1∩X2)<Max(q(X1),q(X2)) | 单因子非线性减弱 |
| q(X1∩X2)>Max (q(X1),q(X2)) | 双因子增强 |
| q(X1∩X2)=q(X1)+q(X2) | 独立 |
| q(X1∩X2)>q(X1)+q(X2) | 非线性增强 |
表2 双因子交互作用类型及判断标准
Table 2 Types and criteria of two-factor interaction effects
| 判断标准 | 交互作用类型 |
|---|---|
| q(X1∩X2)<Min(q(X1),q(X2)) | 非线性减弱 |
| Min(q(X1),q(X2))<q(X1∩X2)<Max(q(X1),q(X2)) | 单因子非线性减弱 |
| q(X1∩X2)>Max (q(X1),q(X2)) | 双因子增强 |
| q(X1∩X2)=q(X1)+q(X2) | 独立 |
| q(X1∩X2)>q(X1)+q(X2) | 非线性增强 |
| 类别 | SD | HD | MD | LD | ND | 合计 | 用户精度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 100% |
| HD | 2 | 48 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 53 | 90.57% |
| MD | 0 | 2 | 88 | 4 | 0 | 94 | 93.62% |
| LD | 1 | 1 | 4 | 52 | 3 | 61 | 85.25% |
| ND | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 17 | 19 | 89.47% |
| 合计 | 6 | 51 | 96 | 57 | 20 | 230 | |
| 生产者精度 | 50% | 94.12% | 91.67% | 91.23% | 85% | ||
| 总体精度 | 90.43% | ||||||
| Kappa系数 | 0.8643 |
表3 2020年 DDI 精度验证Kappa系数
Table 3 2020 DDI accuracy validation Kappa factor
| 类别 | SD | HD | MD | LD | ND | 合计 | 用户精度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 100% |
| HD | 2 | 48 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 53 | 90.57% |
| MD | 0 | 2 | 88 | 4 | 0 | 94 | 93.62% |
| LD | 1 | 1 | 4 | 52 | 3 | 61 | 85.25% |
| ND | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 17 | 19 | 89.47% |
| 合计 | 6 | 51 | 96 | 57 | 20 | 230 | |
| 生产者精度 | 50% | 94.12% | 91.67% | 91.23% | 85% | ||
| 总体精度 | 90.43% | ||||||
| Kappa系数 | 0.8643 |
| 类型 | 2000—2005年 | 2005—2010年 | 2010—2015年 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 面积变化/km² | 动态度/% | 面积变化/km² | 动态度/% | 面积变化/km² | 动态度/% | |
| 极重度 | -44.37 | -4.73 | -1.50 | -0.21 | -60.20 | -8.48 |
| 重度 | -3 681.40 | -4.41 | -1 588.29 | -2.44 | 749.73 | 1.31 |
| 中度 | 895.53 | 0.87 | -1 987.76 | -1.85 | -478.54 | -0.49 |
| 轻度 | 2 308.90 | 5.36 | 3 042.94 | 5.57 | -875.45 | -1.25 |
| 非荒漠化 | 521.33 | 4.64 | 534.61 | 3.87 | 664.46 | 4.03 |
| 类别 | 2015—2020年 | 2020—2022年 | 2000—2022年 | |||
| 面积变化/km² | 动态度/% | 面积变化/km² | 动态度/% | 面积变化/km² | 动态度/% | |
| 极重度 | 79.31 | 19.41 | 70.80 | 21.98 | 44.04 | 1.07 |
| 重度 | -864.80 | -1.42 | -1 847.33 | -8.17 | -7 232.10 | -1.97 |
| 中度 | 20.65 | 0.02 | 80.05 | 0.21 | -1 470.07 | -0.33 |
| 轻度 | -262.16 | -0.40 | 1 347.18 | 5.25 | 5 561.42 | 2.93 |
| 非荒漠化 | 1 027.00 | 5.18 | 349.30 | 3.50 | 3 096.71 | 6.27 |
表4 毛乌素沙地荒漠化土地面积动态变化
Table 4 Dynamic changes of desertification land area in the Mu Us Desert
| 类型 | 2000—2005年 | 2005—2010年 | 2010—2015年 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 面积变化/km² | 动态度/% | 面积变化/km² | 动态度/% | 面积变化/km² | 动态度/% | |
| 极重度 | -44.37 | -4.73 | -1.50 | -0.21 | -60.20 | -8.48 |
| 重度 | -3 681.40 | -4.41 | -1 588.29 | -2.44 | 749.73 | 1.31 |
| 中度 | 895.53 | 0.87 | -1 987.76 | -1.85 | -478.54 | -0.49 |
| 轻度 | 2 308.90 | 5.36 | 3 042.94 | 5.57 | -875.45 | -1.25 |
| 非荒漠化 | 521.33 | 4.64 | 534.61 | 3.87 | 664.46 | 4.03 |
| 类别 | 2015—2020年 | 2020—2022年 | 2000—2022年 | |||
| 面积变化/km² | 动态度/% | 面积变化/km² | 动态度/% | 面积变化/km² | 动态度/% | |
| 极重度 | 79.31 | 19.41 | 70.80 | 21.98 | 44.04 | 1.07 |
| 重度 | -864.80 | -1.42 | -1 847.33 | -8.17 | -7 232.10 | -1.97 |
| 中度 | 20.65 | 0.02 | 80.05 | 0.21 | -1 470.07 | -0.33 |
| 轻度 | -262.16 | -0.40 | 1 347.18 | 5.25 | 5 561.42 | 2.93 |
| 非荒漠化 | 1 027.00 | 5.18 | 349.30 | 3.50 | 3 096.71 | 6.27 |
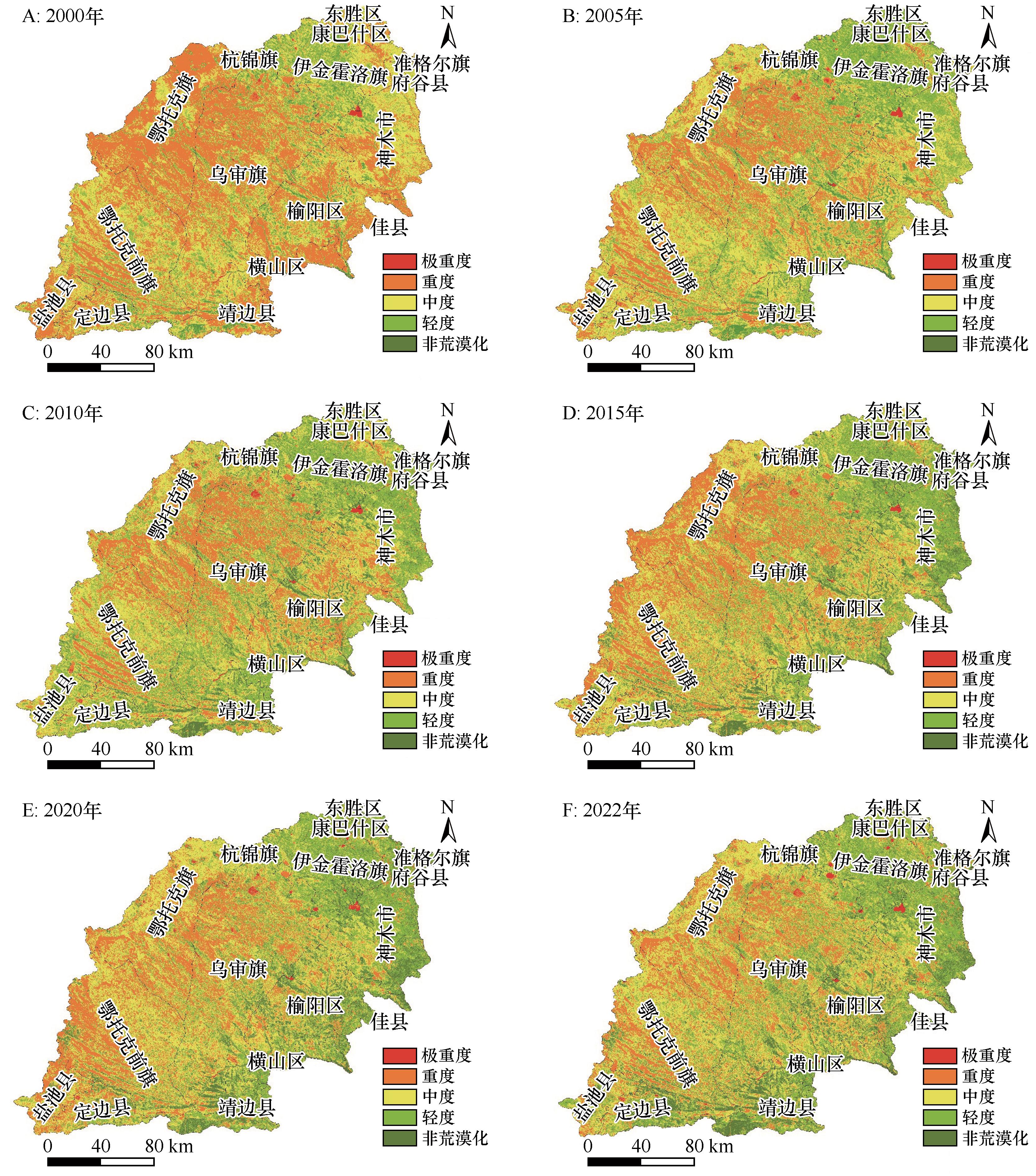
图5 2000—2022年毛乌素沙地土地荒漠化时空分布注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号:GS(2023)2767号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.5 Spatiotemporal distribution of desertification in the Mu Us Desert from 2000 to 2022
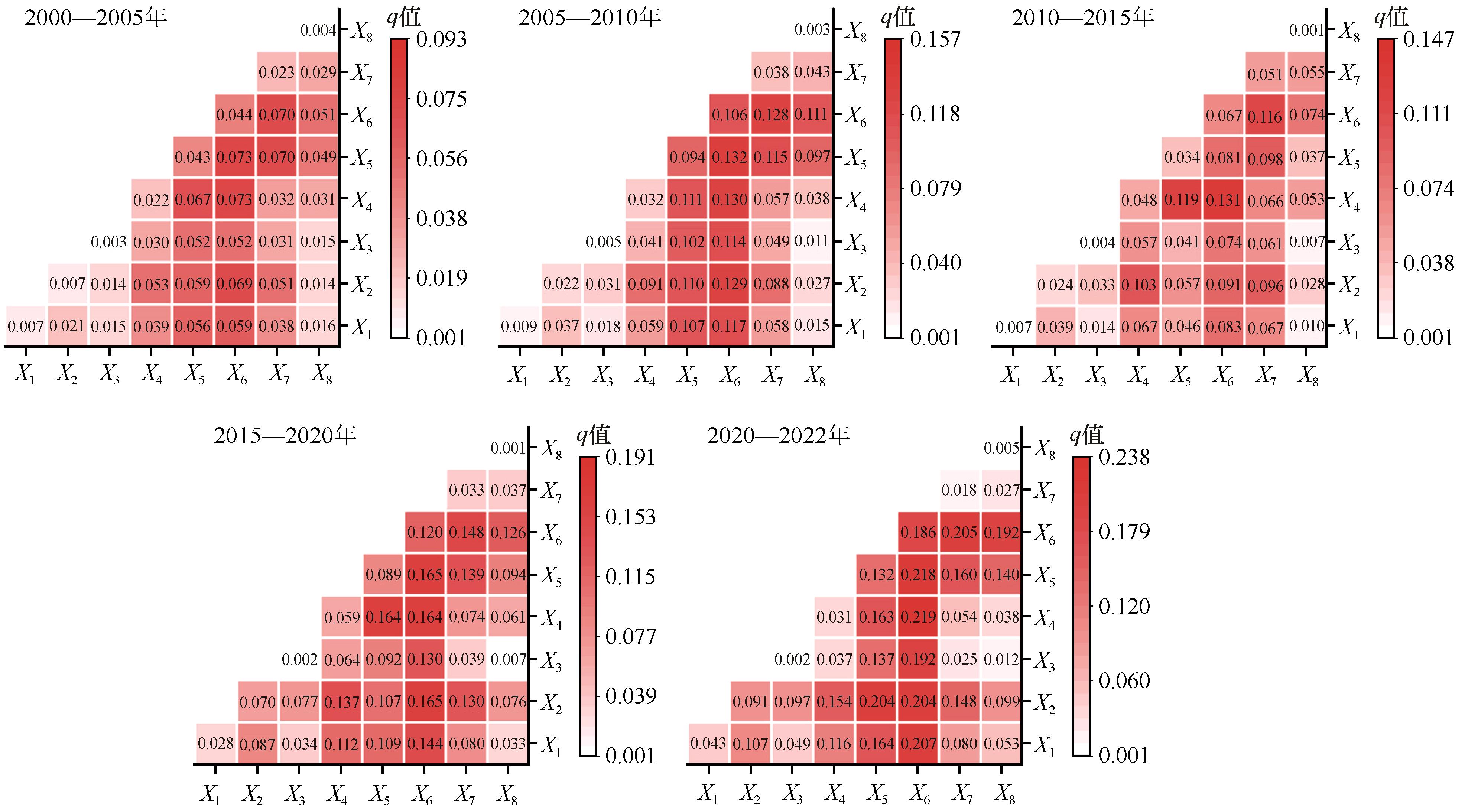
图8 2000—2022年毛乌素沙地荒漠化因子交互探测注:X1-土壤类型,X2-高程,X3-坡向,X4-蒸散发量,X5-降水量,X6-GDP,X7-气温,X8-人口
Fig.8 Interactive detection of desertification factors in the Mu Us Desert from 2000 to 2022
| 1 | 黄进.《环境管理建立防治土地退化和荒漠化良好实践的指南第1部分:良好实践框架》国际标准分析研究[J].标准科学,2020(5):81-86. |
| 2 | 陈宇佳,张俊,张平,等.面向联合国SDG15.3.1的2000~2020年京津冀地区土地退化评估[J].时空信息学报,2023,30(4):560-573. |
| 3 | 董光荣,申建友,金炯,等.关于“荒漠化”与“沙漠化”的概念[J].干旱区地理,1988(1):58-61. |
| 4 | 王涛,朱震达.中国沙漠化研究[J].中国生态农业学报,2001(2):11-16. |
| 5 | 屠志方,李梦先,孙涛.第五次全国荒漠化和沙化监测结果及分析[J].林业资源管理,2016(1):1-5. |
| 6 | 董光荣,高尚玉,金炯,等.青海共和盆地土地沙漠化及其防治[J].中国沙漠,1989,9(1):64-78. |
| 7 | 石建忠,陈翔舜,张龙生,等.甘肃省土地荒漠化状况及分析[J].环境科学学报,2006(9):1539-1544. |
| 8 | 王建宏,张龙生,尚立照.甘肃省沙漠化监测结果[J].中国沙漠,2005,25(5):775-779. |
| 9 | 王建华,李阳,梁树能,等.基于高光谱卫星数据的土地沙化识别及提取研究[J].华北地质,2022,45(4):60-67. |
| 10 | 段英杰,何政伟,诸丽娟,等.基于MODIS的西藏荒漠化动态监测研究[J].广西大学学报(自然科学版),2012,37(2):312-316. |
| 11 | Tomasella J, Silva P V R M, Barbosa A A,et al.Desertification trends in the Northeast of Brazil over the period 2000-2016[J].International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation,2018,73:197-206. |
| 12 | Zhou Y, Hu Z, Geng Q,et al.Monitoring and analysis of desertification surrounding Qinghai Lake (China) using remote sensing big data[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2022,30(7):17420-17436. |
| 13 | 曾永年,向南平,冯兆东,等.Albedo-NDVI特征空间及沙漠化遥感监测指数研究[J].地理科学,2006(1):75-81. |
| 14 | Ma Z, Xie Y, Jiao J,et al.The Construction and Application of an Aledo-NDVI Based Desertification Monitoring Model[J].Procedia Environmental Sciences,2011,10:2029-2035. |
| 15 | Zhou W, Gang C, Zhou F,et al.Quantitative assessment of the individual contribution of climate and human factors to desertification in northwest China using net primary productivity as an indicator[J].Ecological Indicators,2015,48:560-569. |
| 16 | 赵鸿雁,颜长珍,李森,等.黄河流域2000-2020年土地沙漠化遥感监测及驱动力分析[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(3):127-137. |
| 17 | 魏伟,俞啸,张梦真,等.1995-2018年石羊河流域下游荒漠化动态变化[J].应用生态学报,2021,32(6):2098-2106. |
| 18 | 邹明亮,韩雅敏,曾建军,等.基于Albedo-NDVI特征空间的玛曲县荒漠化时空动态监测[J].冰川冻土,2019,41(1):45-53. |
| 19 | 游宇驰,李志威,黄草,等.1990-2016年若尔盖高原荒漠化时空变化分析[J].生态环境学报,2017,26(10):1671-1680. |
| 20 | 毋兆鹏,王明霞,赵晓.基于荒漠化差值指数(DDI)的精河流域荒漠化研究[J].水土保持通报,2014,34(4):188-192. |
| 21 | 闫峰,吴波,王艳姣.2000~2011年毛乌素沙地植被生长状况时空变化特征[J].地理科学,2013,33(5):602-608. |
| 22 | Wang X, Song J, Xiao Z,et al.Desertification in the Mu Us Sandy Land in China:response to climate change and human activity from 2000 to 2020[J].Geography and Sustainability,2022,3(2):177-189. |
| 23 | Li J, Zhao Y, Liu H,et al.Sandy desertification cycles in the southwestern Mu Us Desert in China over the past 80 years recorded based on nebkha sediments[J].Aeolian Research,2016,20:100-107. |
| 24 | Jia X, Fu B, Feng X,et al.The tradeoff and synergy between ecosystem services in the Grain-for-Green areas in Northern Shaanxi,China[J].Ecological Indicators,2014,43:103-113. |
| 25 | Zheng Y, Dong L, Xia Q,et al.Effects of revegetation on climate in the Mu Us Sandy Land of China[J].Science of The Total Environment,2020,739:139958. |
| 26 | Sun Z, Mao Z, Yang L,et al.Impacts of climate change and afforestation on vegetation dynamic in the Mu Us Desert,China[J].Ecological Indicators,2021,129:108020. |
| 27 | 刘庆福.毛乌素沙地沙漠化演变、飞播恢复评估及其对生态系统服务的影响[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古大学,2020. |
| 28 | 杨斐,鹿化煜,吴会娟,等.毛乌素沙地年均水蚀量估算[J].地理学报,2024,79(3):635-653. |
| 29 | 雷金银,吴发启,马璠,等.毛乌素沙地土壤风蚀的气候因子分析[J].水土保持研究,2007(2):104-105. |
| 30 | 贺帅,张成福,洪光宇,等.毛乌素沙地土壤水分研究进展[J].北方园艺,2020(10):138-144. |
| 31 | 王翠萍,韩小红,王昊琛,等.1982-2020年毛乌素沙地植被对气候变化的响应[J].林业资源管理,2023(3):80-89. |
| 32 | 徐新良.中国人口空间分布公里网格数据集[DS].中国科学院资源环境科学数据中心数据注册与出版系统(http://www.resdc.cn/DOI),2017. |
| 33 | Duan H, Wang T, Xue X,et al.Dynamic monitoring of aeolian desertification based on multiple indicators in Horqin Sandy Land,China[J].Science of The Total Environment,2019,650:2374-2388. |
| 34 | 胡海涛.贵州省2001-2020年地表反照率重建及时空演变与影响因素分析[D].贵州:贵州师范大学,2023. |
| 35 | Liang S.Narrowband to broadband conversions of land surface albedo I:algorithms[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2001,76(2):213-238. |
| 36 | Liang S, Shue Y C J, Russ A L,et al.Narrowband to broadband conversions of land surface albedo:II.validation[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2003,84(1):25-41. |
| 37 | Verstraete M M, Pinty B.Designing optimal spectral indexes for remote sensing applications[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,1996,34(5):1254-1265. |
| 38 | 李乃强,徐贵阳.基于自然间断点分级法的土地利用数据网格化分析[J].测绘通报,2020(4):106-110. |
| 39 | 裴亮,陈晨,戴激光,等.基于马尔科夫模型的大凌河流域土地利用/覆被变化趋势研究[J].土壤通报,2017,48(3):525-531. |
| 40 | 王劲峰,徐成东.地理探测器:原理与展望[J].地理学报,2017,72(1):116-134. |
| 41 | Lin M, Hou L, Qi Z,et al.Impacts of climate change and human activities on vegetation NDVI in China's Mu Us Sandy Land during 2000-2019[J].Ecological Indicators,2022,142:109164. |
| 42 | 柏菊,闫峰.2001-2012年毛乌素沙地荒漠化过程及驱动力研究[J].南京师大学报(自然科学版),2016,39(1):132-138. |
| 43 | 闫峰,吴波.近40 a毛乌素沙地荒漠化过程研究[J].干旱区地理,2013,36(6):987-996. |
| 44 | 廉泓林,韩雪莹,刘雅莉,等.基于标准化降水蒸散指数(SPEI)的毛乌素沙地1981-2020年干旱特征研究[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(4):71-80. |
| 45 | 洪光宇,王晓江,苏庆溥,等.毛乌素沙地流动沙丘土壤水分模拟及渗漏特征[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(2):288-298. |
| 46 | Liu Q, Zhang Q, Yan Y,et al.Ecological restoration is the dominant driver of the recent reversal of desertification in the Mu Us Desert (China)[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2020,268:122241. |
| 47 | Ren X, Dong Z, Hu G,et al.A GIS-Based assessment of vulnerability to aeolian desertification in the source areas of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers[J].Remote Sensing,2016,8(8):626. |
| 48 | Hu Y, Han Y, Zhang Y.Land desertification and its influencing factors in Kazakhstan[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2020,180:104203. |
| 49 | D'odorico P, Bhattachan A, Davis K F,et al.Global desertification:drivers and feedbacks[J].Advances in Water Resources,2013,51:326-344. |
| 50 | 李晓岚.毛乌素沙地沙漠化逆转过程及成因分析[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2017. |
| [1] | 马启民, 罗旭冉, 赵人瑰, 王增艳, 余文莉, 贾晓鹏. 毛乌素沙地东北部典型林场新疆杨( Populus alba var. pyramidalis )液流特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(2): 176-183. |
| [2] | 贾虹, 刘连友, 刘吉夫. 共和盆地土地荒漠化敏感性评估[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(1): 1-9. |
| [3] | 刘坤, 王波, 张发国, 吴晓, 王睿, 张峰, 贾蓉, 张红星, 未丽, 董礼, 包爱科. 光伏电站建设的生态效应:光伏治沙研究进展与展望[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(1): 277-291. |
| [4] | 谢佳容, 温小浩, 欧先交, 牛东风, 王双双, 邱明昆. 萨拉乌苏河流域现代沙丘沙钾长石单颗粒释光测年[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(6): 135-145. |
| [5] | 陈兵兵, 盖迎春, 宋忠航, 吴向楠, 艾宇, 杨映, 王生棠, 刘宇烁. 祁连山地区生态质量时空变化及驱动力[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(6): 258-267. |
| [6] | 罗万云, 戎铭倩, 郭世豪. 资源依赖视域下荒漠化地区农户耕地利用效率差异及影响因素研究——基于南疆四地州农户调查数据[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(5): 105-115. |
| [7] | 陈强, 迟洪明, 丁伟, 杨昊天, 吴吉军, 杨奕颖, 吴旭东, 张亚峰, 季波, 李云飞, 张志山, 刘立超. 腾格里沙漠南缘大型光伏基地植被保护和生态修复的理论与对策[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(5): 123-132. |
| [8] | 段翰晨, 黄背英. 基于AHP与改进型MEDALUS模型耦合的科尔沁沙地土地沙漠化敏感性综合评价[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 137-148. |
| [9] | 余吉安, 刘思彤, 史晓蓉, 祁云云. 多元共治模式下企业参与荒漠化治理的理论逻辑、商业模式与经验启示[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 244-252. |
| [10] | 高攀, 崔桂鹏, 孔维远, 周尚哲, 卢琦. “三北”工程山水林田湖草沙“皮”“毛”兼治的生态治理新理念[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 253-261. |
| [11] | 刘二燕, 赵媛媛, 周蝶, 武海岩, 高广磊, 丁国栋. 科尔沁-浑善达克沙地2000—2020年土地沙化时空变化格局[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 46-56. |
| [12] | 杨华庆, 朱睿, 尹振良, 山建安, 张薇, 方春爽. 2001—2020年黄河流域水源涵养区植被覆盖变化及其对气候变化和人类活动的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 57-70. |
| [13] | 申子傲, 吴静, 李纯斌. 2000—2020年河西内陆河流域植被覆盖时空变化特征及其驱动力[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(3): 119-127. |
| [14] | 王佳琪, 李小妹, 刘小槺, 董苗. 毛乌素沙地无定河上游河岸沙丘地貌格局及风水交互作用[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(3): 31-41. |
| [15] | 蔡明玉, 贾飚, 常学礼. 景观格局因子交互作用对科尔沁沙地沙漠化的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(2): 99-108. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
